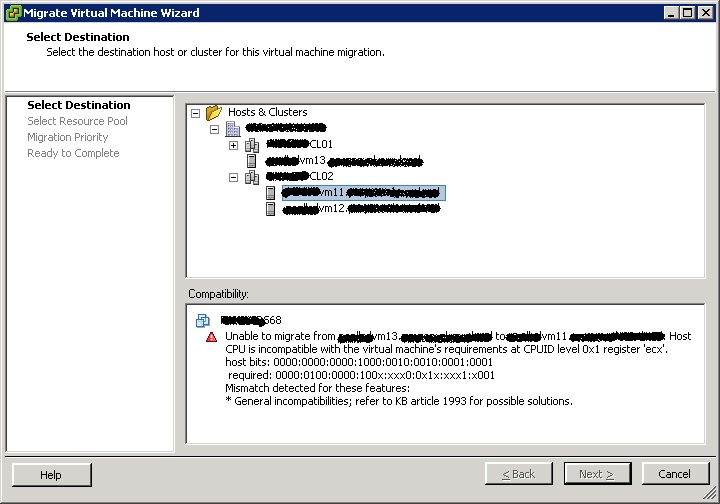
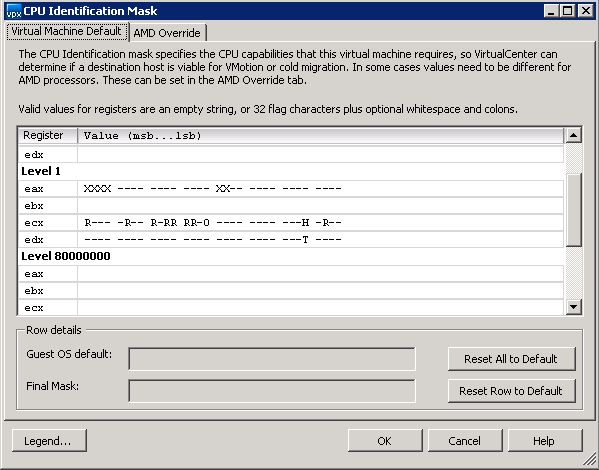
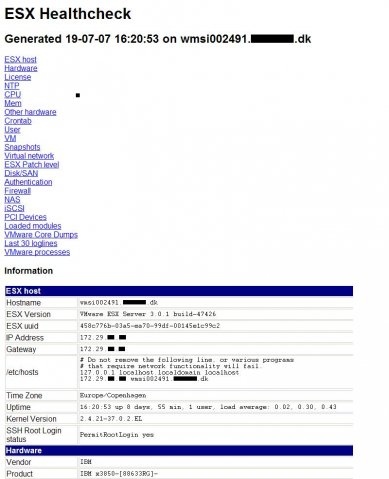
Looking for new scripts i’ve stumbled opon the following script to list all vm’s to an excel sheet and display the total assigned diskspace:
# Define Variables
$outputFile = 'C:\VMDiskCapacity.csv'
$VCServer = "vcenter.mydomain.com"
$username = "vcenter_admin"
$pass = "password"
##################
# Add VI-toolkit #
##################
Add-PSsnapin VMware.VimAutomation.Core
Initialize-VIToolkitEnvironment.ps1
# Connect server
$VC = Connect-VIServer -Server "$VCServer" -User "$username" -Password "$pass"
$myCol = @() # Prepare output collection
$VMs = Get-VM | sort Name # Get all VMs (sorted)
$counter = 0 # Initialize counter for progress bar
ForEach ($VM in $VMs) # Loop through VMs
{
$counter++ # Increase counter for progress bar
Write-Progress -Activity "Gathering disk information" -Status "Processing VM $VM" -PercentComplete (100*($counter/$VMs.count)) # Display progress bar
$myObj = "" |
select VM, TotalDiskSizeGB # Create output object
$myObj.VM = $VM.Name # Virtual Machine Name
$TotalDiskSizeKB = 0
ForEach ($DISK in $VM.HardDisks) # Loop through VM's harddisks
{
$TotalDiskSizeKB += $DISK.CapacityKB
}
$myObj.TotalDiskSizeGB = [math]::Round(($TotalDiskSizeKB * 1KB / 1GB),0) #Disk Size in GB
$myCol += $myObj # Add output to collection
}
$myCol | Export-Csv $outputFile -NoTypeInformation # Export output to csv